
1 Synology White Paper
White Paper
Synology Drive
White Paper
Powerful
Content Collaboration Tools for Business
Table of
Contents
Introduction
02
Software Architecture
03
Architecture of the Drive Server
Architecture of the Drive Clients
Achieving Optimal Business Productivity
06
Centralized File Management
Real-Time Syncing and Backup
Teamwork and Collaboration
Multi-Site Coordination
Hybrid Cloud
Syncing, Sharing, and Security
10
Synchronization Mechanism
Permission and Sharing Mechanism
Security Mechanism
Fulfilling Modern Workplace Needs
16

02 Synology White Paper
Introduction
Business Challenges
The rising popularity of cloud services has transformed team
collaboration from accessing and sharing files anywhere,
anytime to content-centric collaboration. In 2017, Gartner
renamed the enterprise file synchronization and sharing market
to content collaboration platform (CCP) market in response to
the evolution of market applications, with CCP defined as a range
of content-centric platforms enabling secure file productivity and
content collaboration for individuals and teams.
1
While cloud
service deployments can be in public cloud, hybrid cloud, private
cloud, or on-premise platforms, many of such platforms lack
powerful enough features for effectively locating certain files,
collaborative editing by multiple users, and customizable access
control rules.
Synology Solutions for Content Collaboration
Synology is committed to developing a CCP to meet the common
corporate demands for file collaboration, sharing, and syncing.
Synology Drive is an all-round file management solution that
comes with Synology NAS. It unifies multiple file portals on
Synology NAS and serves as a centralized file portal where
users can access, sync, and share files from web browsers,
computer clients, and mobile apps with customized settings
anytime and anywhere, thereby increasing work efficiency and
productivity.This white paper details Synology Drive’s design
and architecture, features and technologies, and common usage
scenarios.
Contrary to most on-premise clouds which require expensive
and dedicated infrastructure, Synology Drive is available on most
Synology NAS models and can beintegrated with enterprises’
existing business environments, such as Windows AD or LDAP,
saving the hassle of switching to or purchasing other systems.
Drive comes with an intuitive user interface for managing
collaboration tools,simplifying data management on Synology
NAS, and syncing data across multiple devices. To maximize
its value and functionality, Drive is integrated with several
DiskStation Manager (DSM)packages, including Synology Office
2
,
Synology Universal Search
3
, and Synology Hyper Backup
4
.
Introduction
Key features of Synology Drive:
• Real-time synchronization:Automates data synchronization
in real-time among the supported and connected client
devices (i.e., Windows PC, Mac, Linux computers, and
Synology NAS).
• File versioning:Retains up to 32 historical file versions and
keeps unlimited Office file versions.
• Permission and sharing:Allows administrators to assign sync
permissions that restrict users to one-way syncing or syncing
files of specific size and types.
• Instant file syncing and backup:Continuously monitor and
instantly sync or back up file changes through its clients.
• Enhanced security:Allows administrators to configure sync
profiles for centralized control and to track the IP addresses
and locations of all connected devices.
• Optimized search quality:Provides a full-text indexing
engine to elevate content search speed and quality.
• Customizable file/folder categories: Allows users to star,
label, and categorize files and folders to instantly find specific
contents over a massive amount of data.
• Anywhere mobility:Pins files from the server to mobile apps
and syncs up-to-date file versions automatically, ensuring
that users can browse the latest files even when offline.
1.
Hobert, K., Basso, M., Woodbridge, M. (2017, September 12). Critical Capabilities for
Content Collaboration Platforms.
2.
Synology Office provides professional editing tools for creating work documents
with ease and efficiency. Its real-time synchronization and collaboration features
instantly sync files across multiple platforms and allow multiple users to
simultaneously collaborate on the same file, ensuring data security while boosting
productivity. Clickhere to learn more.
3.
Synology Universal Search offers global search into applications and files on
Synology NAS, allowing users to index folders to perform a deep search by file name
or by file content and to find files on Drive within a few clicks.
4.
Synology Hyper Backup is a comprehensive backup solution capable of retrieving
data from multiple recovery points through minimal storage consumption. It offers
schedulable backup plans, multi-version backup, flexible backup rotation, and more.
Clickhere to learn more.
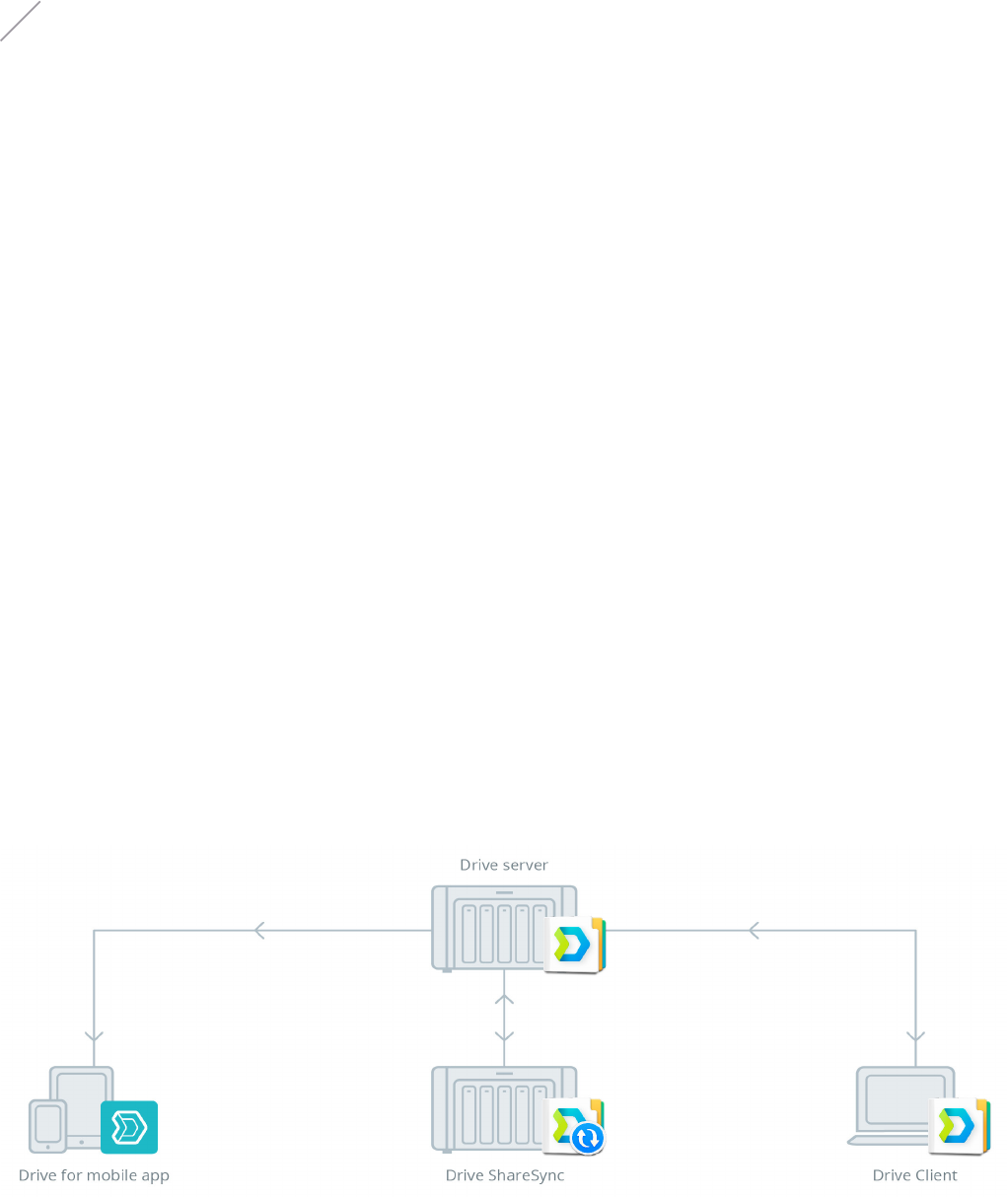
03Synology White Paper
Software Architecture
Synology Drive is compatible with DSM 6.2.2 or above and
is supported on various browser types, including Firefox,
Chrome, Safari, and Internet Explorer 10 or later. It comes with
acomprehensive suite of packages and clients that can be
flexibly applied to different workplace scenarios:
• Package: Synology Drive Server - DSM package which consists
of below components
• Synology Drive: A centralized web portal for file
collaboration, management, and synchronization, and for
controlling all the connected clients.
• Synology Drive Admin Console: A control panel designed
for system administrators to monitor the system and
manage data versioning and recovery.
• Synology Drive ShareSync: An application which supports
one-way and two-way synchronization to flexibly sync
shared folders between one Synology NAS and another.
Software Architecture
Figure 1: Architecture of the Drive suite
• Native clients
• Synology Drive Client: A desktop client utility developed
to facilitate file syncing, sharing, and collaboration
between a centralized Synology NAS and multiple client
computers.
• Synology Drive - mobile app: A mobile app available on
Android and iOS platforms, and is capable of syncing
files to local devices, allowing users to browse the files
anytime, anywhere.
Architectures of the Drive server and sync clients are provided in
the following sections.
04 Synology White Paper
Software Architecture
Synology Drive Server runs on DSM and is protected by network
security features such as firewall, autoblock, account protection,
denial-of-service (DoS) protection, and two-factor authentication,
while data security is ensured with encrypted shared folders,
RAID configurations, UPS support (external), and various offsite
backup options.
5
The server package is the control center of all
the connected clients and is designed to authenticate clients,
control the synchronization process, and maintain version
histories through the following five main components:
• Web portal interface: Built with an interactive web interface
for users to easily manage the files on Drive.
• Package backend service: Handles multiple types of incoming
client requests such as file operation and push notifications.
• Versioning database: Keeps track of synchronization status
and file versions.
6
• Authentication service: Authenticates client requests by
comparing DSM privileges.
• File system monitoring service: Monitors the file changes in
DSM’s shared folders.
With file changes committed to a versioning database, the
Drive server is capable of managing the modifications made
in shared folders via all the protocols compatible with DSM
(e.g., SMB, AFP, FTP, and WebDAV). Compared with most of the
file synchronization software available on the market, Drive’s
compatibility with various types of protocol ensures that it can
seamlessly integrate with enterprises’ existing environments.
7
The Drive clients sync data between computers, Synology NAS,
and ShareSync and are comprised of the following components:
• Local event monitoring: Monitors file changes on the local
file system.
• Remote file change monitoring: Requests file changes from
the server.
• Synchronization database: Maintains the synchronization
status of the clients.
• Synchronization process: Communicates with the server and
syncs files.
• User interface: Offers an intuitive control panel with overlay
icons for managing task syncing, information tray menu, and
sync status.
The intuitive design of the Drive mobile app also supports the
aforementioned synchronization database and process, syncing
files from the server to ensure that users can browse the latest
files on their mobile devices even without network connection.
The Drive clients are supported on the following operating
systems (OS):
• Synology NAS (DSM 6.2.2 and onward)
• Windows (Windows 7 and onward)
• Mac OS X (10.11 and onward)
• Ubuntu 16.04 and onward (official versions)
8
• iPhone, iPad, and iPod touch running on iOS 9.0+
9
• Devices running on Android 5.0+, with touchscreen and Wi-Fi
capabilities (issues strictly related to device compatibility may
not be handled for non-mainstream devices)
Architecture of the Synology Drive Server Architecture of the Synology Drive Clients
5.
DSM firewall provides basic options to prevent unauthorized login and control
service access, and network ports can allow or deny specific IP addresses. The
autoblock feature improves the security of Synology NAS by blocking clients’ IP
addresses with too many failed login attempts, thereby preventing accounts from
being broken into via brute-force attacks. DoS prevents malicious attacks over the
Internet and adds an extra layer of protection to Synology NAS and DSM.
6.
Files in the Office package are kept in the versioning database.
7.
The number of concurrent connections supported by Synology Drive varies
according to the physical capability and loading of the server.
8.
Synology Drive only supports Ubuntu with the latest release and latest LTS release.
9.
Mobile apps are available at built-in application stores, and MSI, EXE, DMG, and DEB
installers are offered for computer platforms at Synology’s Download Center. The
supported OS versions are subject to change with each software release.
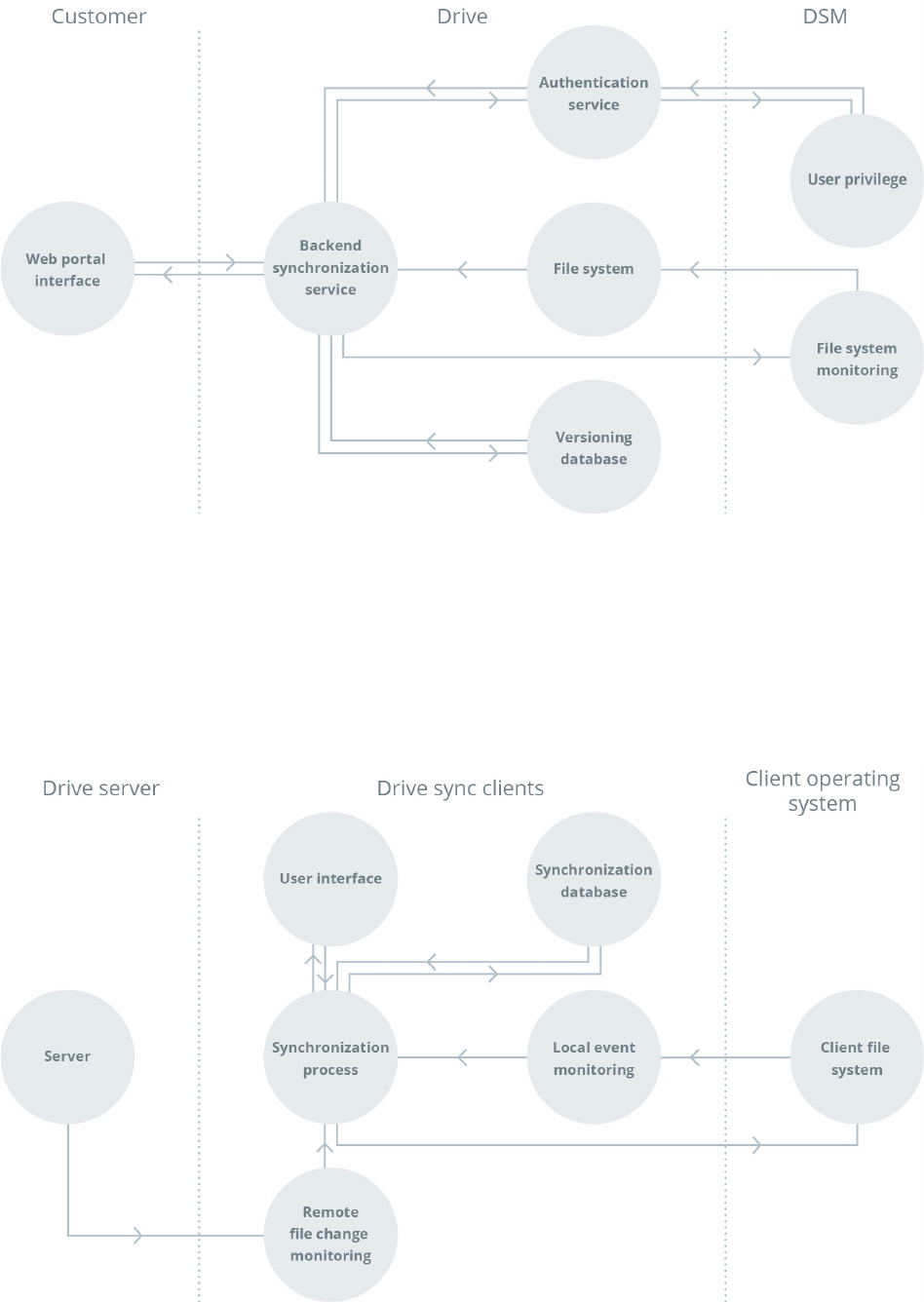
05Synology White Paper
Software Architecture
Figure 2: Architecture of the Drive server
Figure 3: Architecture of the Drive sync clients
06 Synology White Paper
Achieving Optimal Business Productivity
With Drive serving as a platform for centralizing data, Synology
NAS is the next-generation file server designed to solve common
management challenges including the rising Bring Your Own
Cloud (BYOC) trend. In addition to data centralization, Drive
offers file management and synchronization solutions to
provide a unified portal for accessing files on NAS. With all the
data stored on the on-premise cloud, employees can simply
browse files via any mainstream web browsers. Files can also
be managed and shared simply through Team Folder and the
customizable labels on Drive, without the hassle of storing files
on external devices or attaching files to emails.
Our versioning technology allows corporate users to retain
multiple versions of file copies on a centralized portal and
effortlessly retrieve specific versions whenever needed. For a
company needing to keep multiple file versions for different
purposes, the First-in-first-out rotation policy is suitable for
Achieving Optimal
Business Productivity
Centralized File Management
Synology Drive is designed to optimize the overall workplace
productivity. Its architecture is compatible with most existing
business environments and its robust features are adaptable to
various workplace scenarios requiring file synchronization and
backup, cross-site collaboration, hybrid cloud integration, and
more.
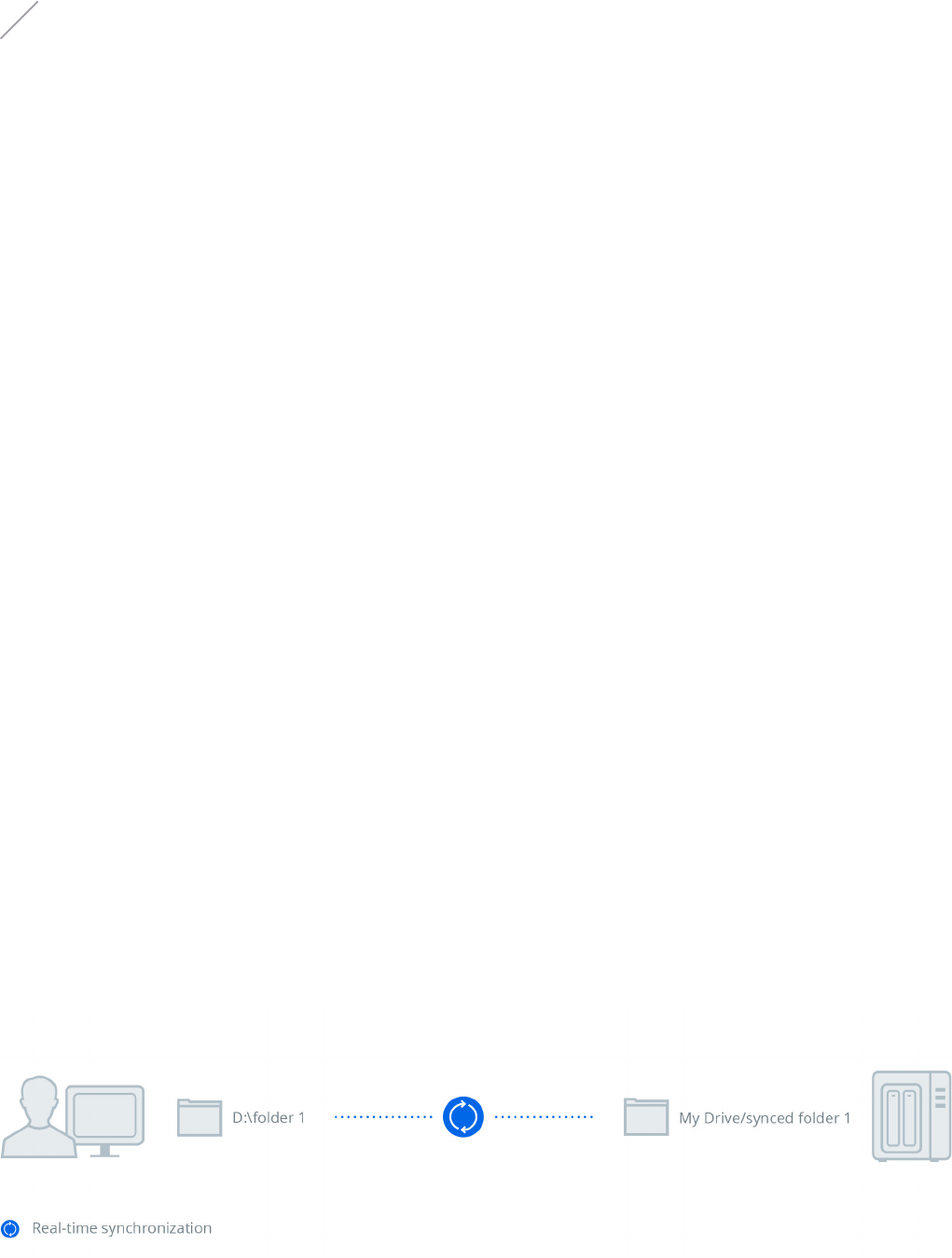
Figure 4: Synchronization
keeping the most recent file copies, such as annual financial
reports updated regularly at the end of every year. Our patented
Intelliversioning technology retains the most important file
versions and can be applied to files modified during a specific
time period. This feature, for example, can be used when users
need to modify a press release article numerous times to
produce a top-notch article within three days before a product
launch. Please see the Synchronization Mechanism section for
technical details.
07Synology White Paper
Achieving Optimal Business Productivity
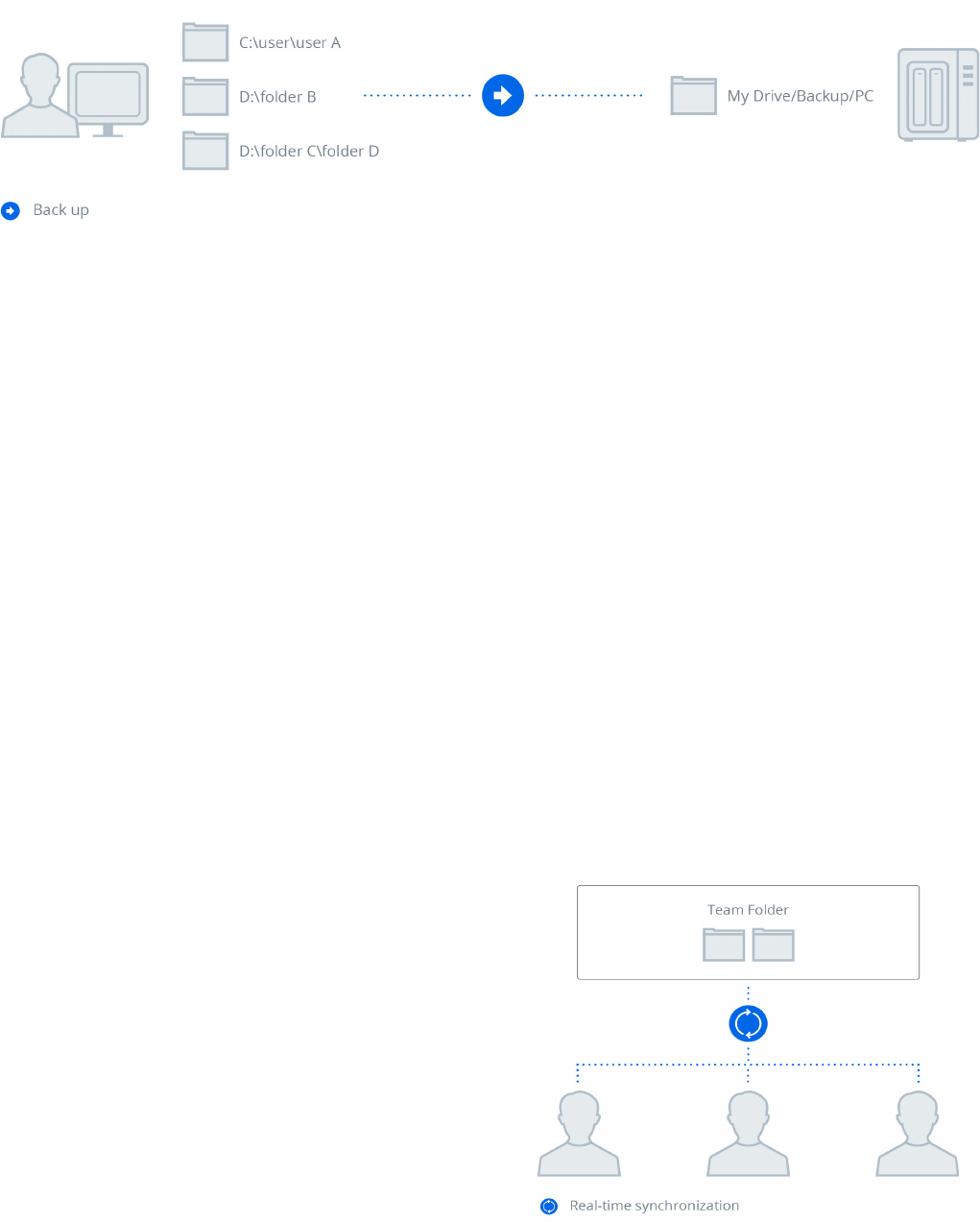
The flexible sharing options make Drive particularly
advantageous for businesses frequently engaged in internal or
external collaborations. Drive works seamlessly with the Linux
and Windows access control list (ACL) privilege rules on DSM and
can grant different levels of privilege to users, allowing those
with read and/or write privileges to sync the files within Team
Folder.
12
IT administrators merely need to set ACL permissions when
collaborating within an organization, and the collaborators on
the same projects can fully manage Team Folder by specifying
which users are granted permissions to download or sync
certain folders. The folders and files in Team Folder will still be
retained even if the owners leave the team.
Teamwork and Collaboration
Real-Time Syncing and Backup
The cross-device data synchronization feature ensures efficient
work productivity even when employees work away from the
office because a centralized Synology NAS can sync data to and
from multiple client computers and Synology NAS. In addition,
data are synced to mobile devices to ensure that files can be
browsed even when the devices are offline. Data are seamlessly
synced among these devices with Synology NAS serving as the
host server and other paired devices acting as the clients. Users
who are working remotely or partnering with external clients
can simply connect to the Synology NAS server at their office
via QuickConnect
10
or Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS)
11
,
thereby retrieving the most up-to-date files. Administrators on
the server-side are able to control the bandwidth and manage
connected clients, while users on the client-side can set the sync
criteria, such as selecting specific folders and setting the file size
and types for syncing.
Synology Drive Client allows users to instantly back up files
or schedule backup tasks from multiple client computers to a
centralized Synology NAS. A backup version is created and saved
every time a file is modified, allowing users on client computers
to browse historical versions of the backed-up data and restore
them to a specific version whenever needed, minimizing the
chance of accidental data loss and simplifying file version
management. Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) on Windows
ensures that locked files can still be backed up, and thus
companies which view confidential data as the most imperative
asset no longer need to worry about threats from malicious
attacks such as ransomware. Please see the Synchronization
Mechanism section for technical details.
10.
QuickConnect offers a relay service that allows Synology NAS to be accessible over
the Internet without actually setting up a static IP address, making it possible to
keep the NAS server within a local area network and allowing Drive to be accessed
over the Internet using QuickConnect.
11.
DDNS simplifies connection to your Synology NAS over the Internet by mapping a
hostname to its IP address.
Figure 5: Backup
12.
Administrators can enable Shared Folder in DSM as Team Folder in Drive Admin
Console, with Team Folder serving as a shared folder for team members to manage
the files within.
Figure 6: Team Folder coordination
08 Synology White Paper
Achieving Optimal Business Productivity
For companies with branches in different locations which host
their own servers, Drive is a particularly efficient solution for
cross-site collaboration. The integration with Synology Drive
ShareSync allows employees to connect to and sync files to
Drive in real-time. A centralized Synology NAS can sync data
to its multiple clients, ensuring that a backup version of a file
is always safely secured on a remote Synology NAS. Access
privilege can be configured to only allow one-way download
when headquarters push files to its local branches, and to allow
two-way syncing when employees collaborate on files between
two sites. Please see the Synchronization Mechanism section
for technical details.
A multi-site deployment where Drive ShareSync runs in every
regional office and is linked to the central Drive server at
headquarters offers several advantages:
• Reduces upload bandwidth of headquarters because files
only need to be synced at the headquarters once, saving
regional offices the hassle of individually downloading files
from the headquarters.
• Allows independent IT administrators flexible privilege control
in each regional office.
• Optimizes storage by syncing data selectively according to the
characteristics and scales of regional offices.
• Allows files to be synced via Drive and enables employees in
remote branches to access local servers efficiently.
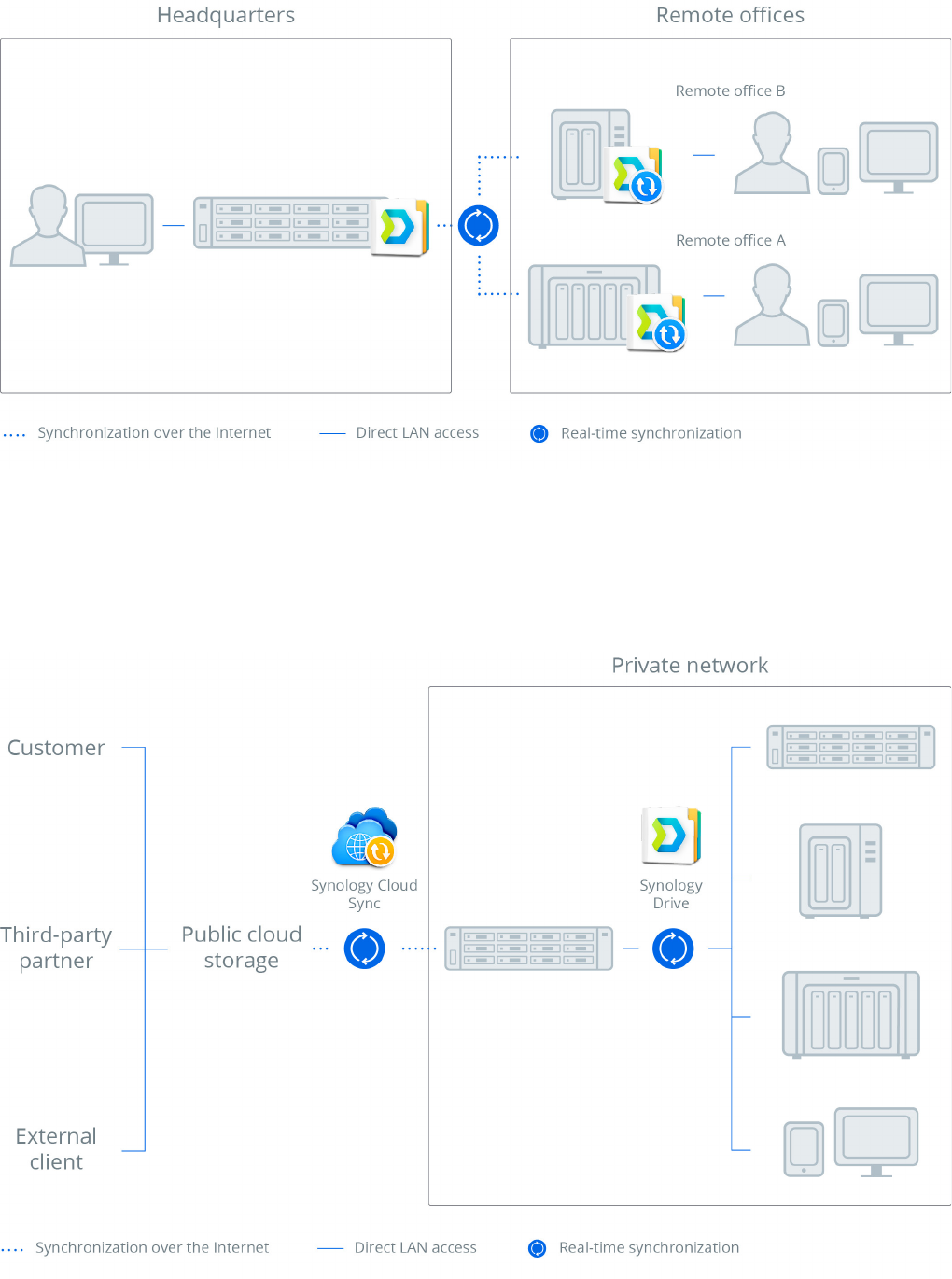
Multi-Site Coordination
Hybrid Cloud
Businesses nowadays are driven to improve data access and
synchronization speeds while ensuring adequate data security
and classification, particularly when collaborating with their
partners. Drive users can use the Cloud Sync features to sync
their Synology NAS with public cloud services such as Dropbox,
Google Drive, OneDrive, and Amazon S3-compatible storage.
13
These features ensure seamless compatibility and effective
work productivity through the use of third-party tools. The
purpose of syncing Synology NAS with another public cloud is
to leverage its massive bandwidth and availability. By sending
files to public clouds, Cloud Sync offloads insensitive data
shared from company servers and keeps the servers at a highly
secure level, denying direct access from outside the corporate
network. Corporate partners can use the web interfaces that
they are familiar with to fetch the files shared with them from
public clouds. Enabling the encryption feature allows Cloud Sync
to transform public cloud storage services into secure offsite
data backup destinations. Please see the Synchronization
Mechanism section for technical details.
13.
Please refer to this page for a list of public cloud services which Cloud Sync can
sync with.
During inter-organizational collaboration, users can customize
file sharing options and assign file or folder access privileges to
external users either with or without DSM accounts. File sharing
links can be further protected with a password and even deleted
after a set expiration date, thereby adding an extra layer of
protection to sensitive data. The comprehensive integration with
Synology Office allows Drive to fulfill the growing demands for
office data collaboration. For content publishers who frequently
exchange numerous magazine article documents with their
clients, the sharing options allow both parties to collaborate
seamlessly on documents. Passphrases and expiration dates
can also be set to prevent any information leakage before the
articles are published to the public. Please see the Security
Mechanism section for technical details.
09Synology White Paper
Achieving Optimal Business Productivity
Figure 8: Hybrid cloud
Figure 7: Multi-site coordination
10 Synology White Paper
Syncing, Sharing, and Security
Data synchronization, access permission, sharing, and security
are major technologies adopted to ensure that Drive centralizes
file management, integrates with third-party tools, simplifies
cross-site deployments, enhances real-time collaboration, and
more. This chapter details the mechanisms and technologies
behind these Drive features.
Syncing, Sharing, and
Security
Synology Point Recovery (SPR), Delta Sync, versioning, and
selective sync are the technologies behind the server-to-server,
server-to-client, and data-to-data syncing features. These
technologies are adopted to fulfill all synchronization demands
for real-time collaborations within an organization, outside of an
organization, among different sites, with public cloud services,
and more.
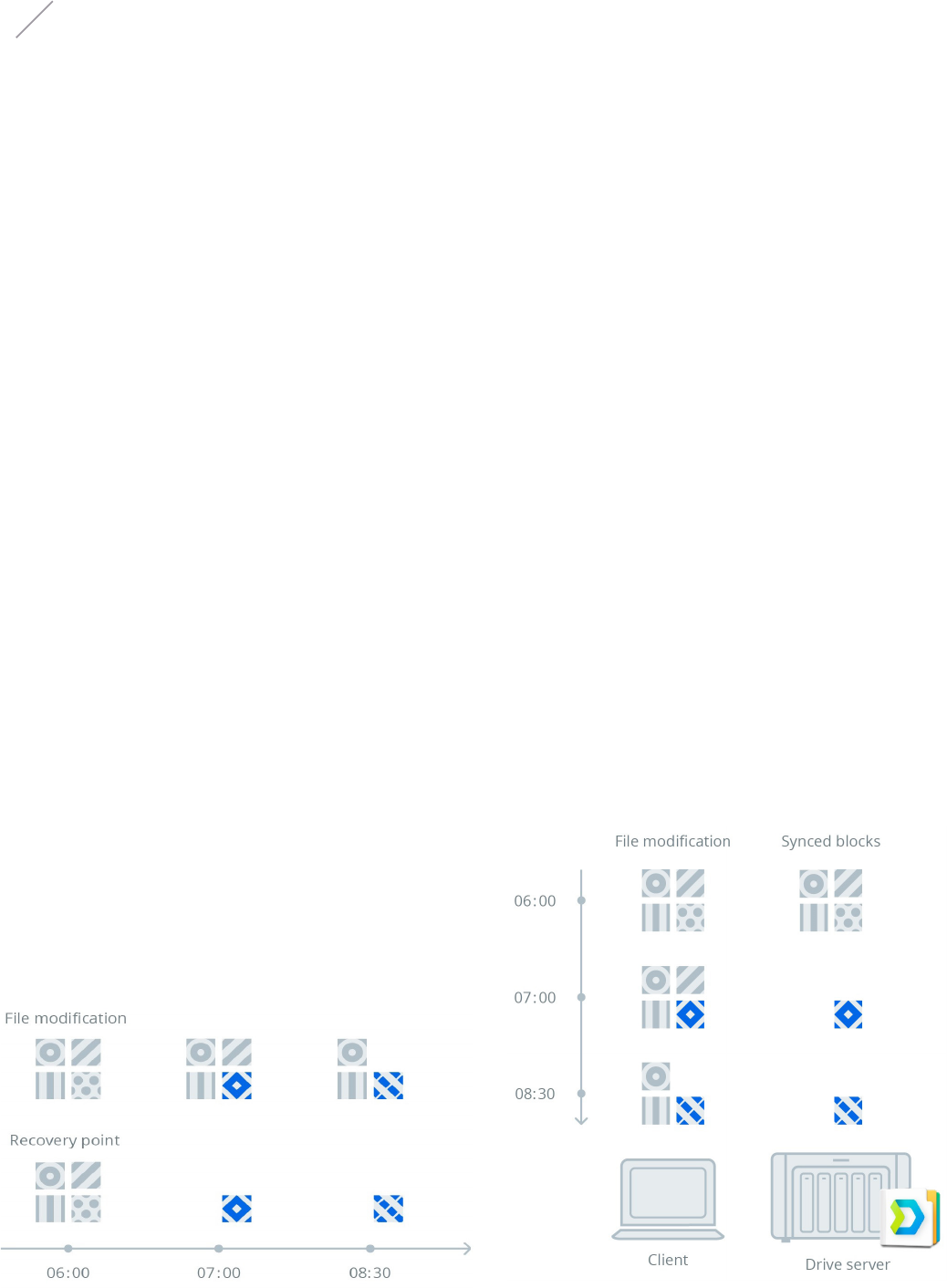
Synchronization Mechanism
The SPR technology is developed with the purposes of keeping
multiple file versions to ensure data safety while creating precise
recovery points to optimize resource usage. File modification
constitutes a recovery point in time that roughly translates to
a snapshot of a volume. A recovery point consists of a "patch"
that defines the difference from its preceding recovery point.
SPR is associated with several benefits. Instead of keeping every
file version in its entirety, Drive maintains historical versions
Synology Point Recovery
Figure 9: Synology Point Recovery
In response to employees' needs to update large files regularly,
Drive adopts Delta Sync to accelerate synchronization speed and
save bandwidth. When a file is modified, Delta Sync only syncs
the modified file parts instead of the whole file. Hence, before
a modified file is uploaded to or downloaded from the Drive
server, Delta Sync compares the new version with the previous
one and only transfers the corresponding file changes by
patches, thus considerably reducing the size of the transferred
data.
Delta Sync
Figure 10: Delta Sync
incrementally, with every version linked to the previous version
by the patch. The patches also contribute to a highly efficient
and storage-saving way of maintaining the database for version
retrieval or restoration. Only the modified bytes found between
each version need to be transmitted upon update, thereby
reducing the network traffic considerably. SPR operates with the
assistance of Drive's file system monitoring and file modification
notification features on both the server and client sides.
11Synology White Paper
Syncing, Sharing, and Security
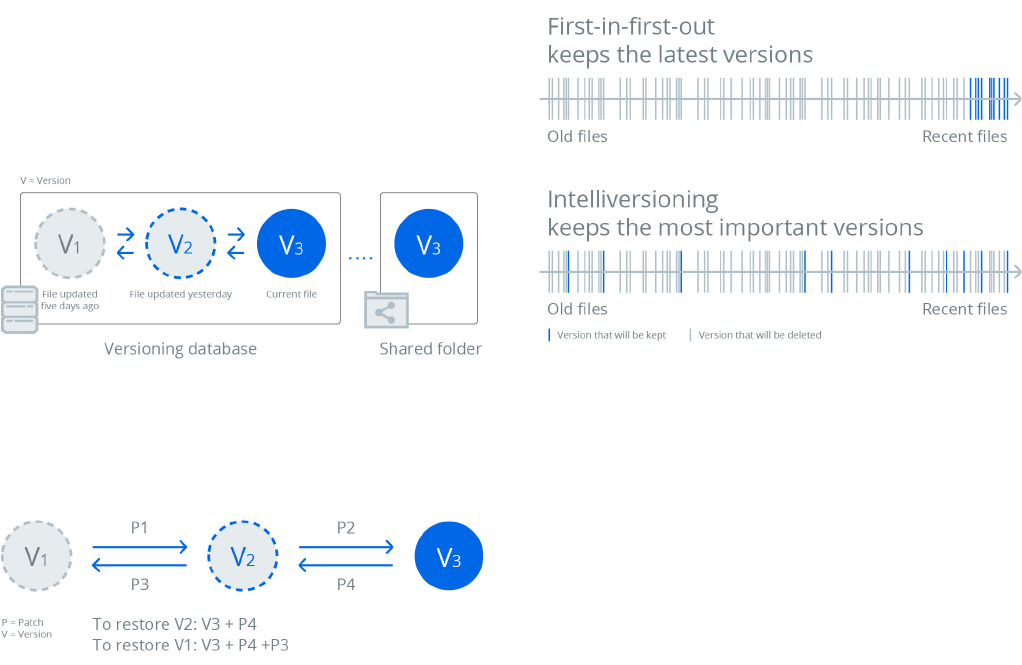
File versioning tracks file changes made over time and allows
historical versions to be restored or fetched when needed.
Drive supports up to 32 historical versions and the version
number for each shared folder is customizable. It also leverages
the efficiency of SPR to reduce storage consumption while
maintaining historical versions. The Drive server database keeps
a copy of every present file in the synchronized shared folder
to avoid permanent data loss caused by operational mistakes.
All the preceding versions consist merely of file properties (i.e.,
attributes) while adjacent versions are linked by patches, which
define the transformation steps between versions and allow
historical versions to be restored recursively.
Versioning
Figure 11: Versioning
Figure 12: Version advancement and restoration
Version Rotation
Version rotation is triggered when the version count of a file
reaches its limit. The Drive server implements two algorithms to
manage version rotation:
• First-in-first-out:
When the number of versions reaches the maximum limit,
this algorithm rotates the oldest version once a new version
is added to the versioning database. This algorithm is simple
and is suitable for files that are not prone to change, such as
music or video files.
Figure 13: Version rotation
Btrfs Integration
Btrfs is an advanced file system on Linux that supports storage
features such as pooling, snapshot, and compression.
14
On a
Btrfs volume, Drive leverages snapshot technology to create
copies of the present files in shared folders and store them
in the database according to the copy-on-write principle.
Compared with the ext4 file system that requires a full copy of
the present file in the database, the Drive database on a Btrfs
volume contains only snapshots (for present files) and patches
(for preceding files), thus saving the storage space up to 50%
when storing historical file versions.
14.
Please see this FAQ to understand which Synology NAS models support the Btrfs
file system.
• Intelliversioning:
Synology developed this algorithm to smartly manage
historical versions, allowing a limited number of versions
to span over a longer period of time and retaining the most
significant versions in the file history. This algorithm is
particularly suitable for files that are prone to change, such as
files that are changed during a specific time period or under
different frequency.
12 Synology White Paper
Syncing, Sharing, and Security
Selective Synchronization
Client-Side Selective Sync
Users on the client side can leverage the selective sync feature
to sync only the required data. Selective sync is comprised of
different rules that function as a filter for the sync process.
Whenever a file or folder syncing operation begins, all the
selective sync rules are applied to check whether the sync
process should be blocked.
15
The following selective sync rules
are currently supported:
1. Folder path
2. Filename globbing
3. File size
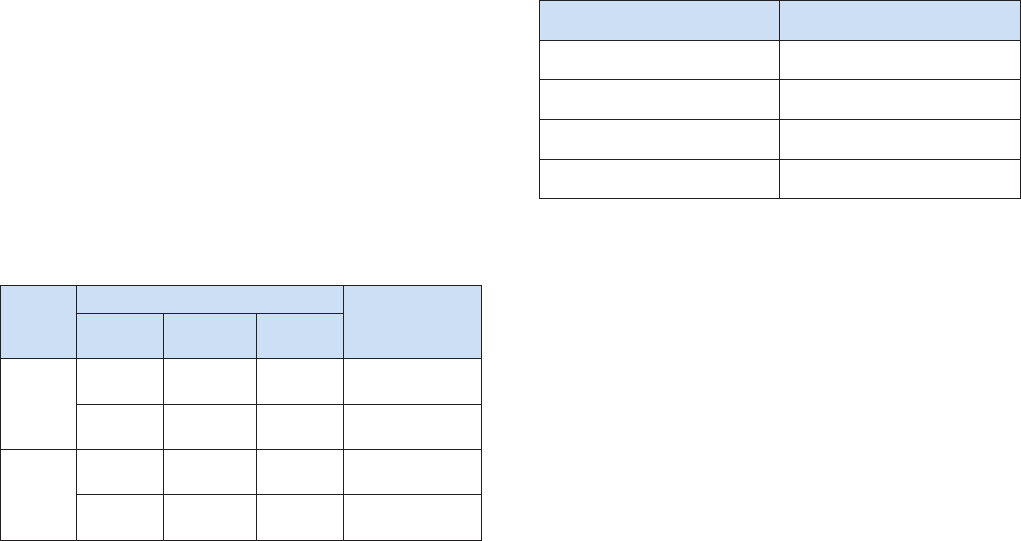
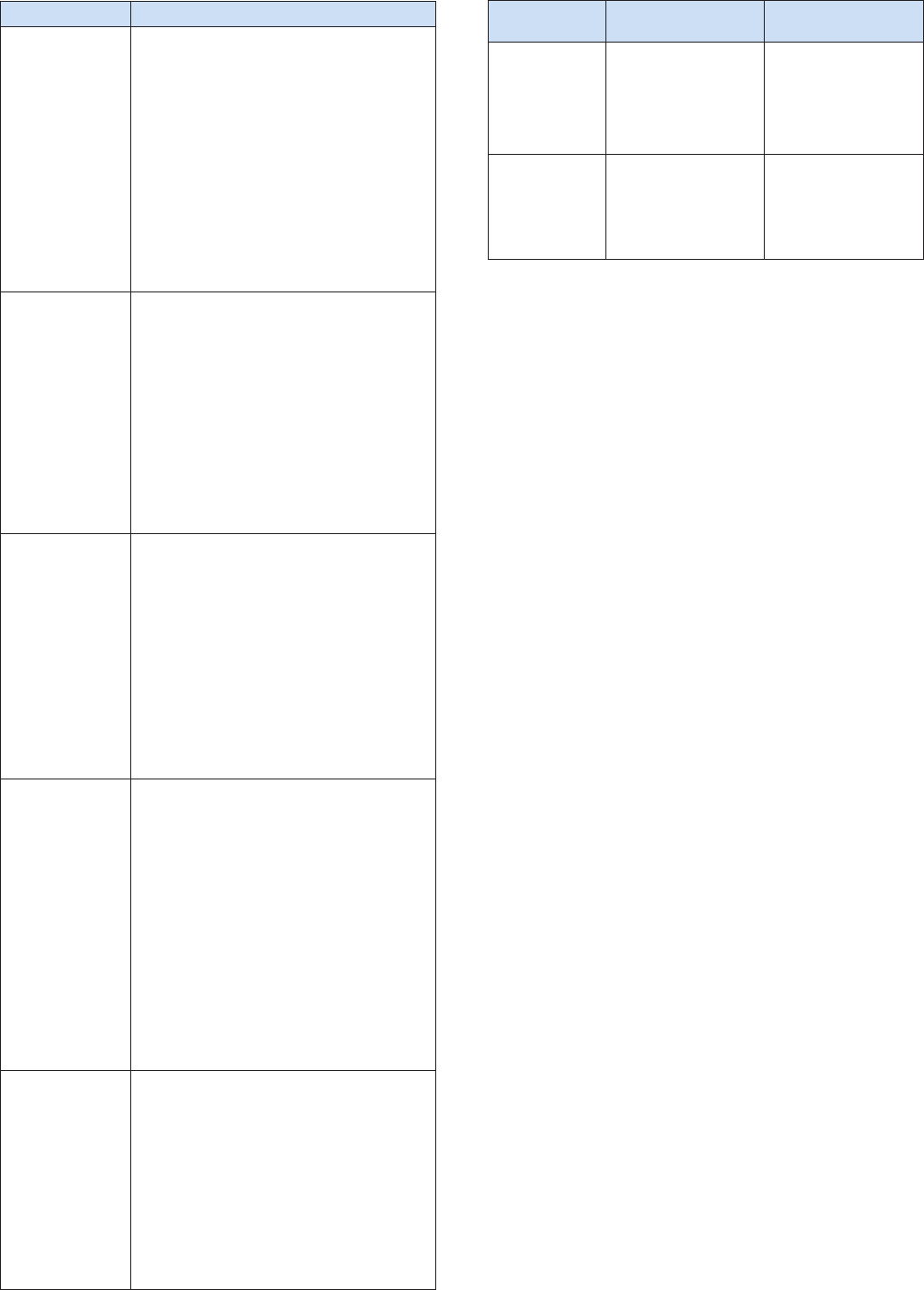
Table 1 provides an example of how the selective sync rules are
checked:
File
Selective sync rules
Result
File path
Filename
globbing
File size
/a/b.txt
Folder /a None None Not synced
None
*.txt or b.*
or b.txt
None Not synced
/a/b.txt
(10KB)
None None > 1 KB Not synced
Folder /b
or /c
*.doc or
d.txt
< 100 KB
Passed the check,
will be synced
Server-Controlled Sync Profile
Administrators can set up sync profiles to control the files and
folders that will be synced by a specific user. Sync profiles are a
set of sync rules that are similar to the sync rules on the client
side. The following rules are currently supported:
1. File type
2. Filename globbing
3. File size
Whenever the sync profile on the server is changed and applied
to an account, clients owned by the account will be compelled to
adopt the same rules during data synchronization.
The sync profile rules are checked on both the client and server
sides. To achieve maximum efficiency, the rules are first checked
on the client side when a file or folder is to be synced, so as to
determine whether to continue the sync process. The rules are
also checked on the server side upon each file operation request
to avoid malicious clients. The double checking mechanism
ensures that the sync profile mechanism is highly secure and
efficient. Drive combines the sync profile mechanism and ACL
privilege control, allowing administrators to flexibly control the
synchronization behavior of all the connected clients (please see
Table 2):
Sync behavior control Method
Folder-level access / sync control ACL privilege
File-level access / sync control ACL privilege or sync prole
File type sync control Sync prole
File size sync control Sync prole
Drive grants comprehensive privileges for IT administrators
to authenticate user identity, customize user privilege,
control sharing options, as well as monitor server activities
and client lists to track the connected devices. Because Drive
works seamlessly with the shared folder privileges on DSM, IT
administrators can leverage the existing DSM accounts for file
services and synchronization, without the hassle of maintaining
another set of user accounts for third-party synchronization.
Permission and Sharing Mechanism
Identity Authentication and Privilege Control
All synchronization abides by ACL and Linux permissions
assigned in DSM. Administrators can go to Shared Folder in
DSM to configure the read and write privileges of Team Folder
in Drive, thereby allowing team members with ACL privileges
to manage the files within Team Folder. When setting access
privileges, administrators can assign read-only permissions to a
Team Folder for specific users to ensure one-way syncing, and
can configure sync profiles to limit users to only sync files of
certain size and types. Access privileges are granted as a result of
the combination of ACL and Team Folder privileges (ACL or UNIX
permissions or both, depending on the Team Folder settings).
When a client issues a request, the Team Folder privileges are
first examined, and ACL privileges are subsequently examined.
Users require sufficient privileges for each request to be allowed
to sync files and folders. Table 3 shows the ACL privileges
required for each file operation, and Table 4 shows the Team
Folder privileges required for each file operation.
15.
All the folders on the client side are by default synchronized unless selective sync
rules are explicitly specified.
Table 1
Table 2
13Synology White Paper
Syncing, Sharing, and Security
Operation ACL privilege
All operations
Users need either of the following two privileges
to all the parent folders to ensure access to the
directory (directory check):
1. Write privilege of parent folders
2. For parent folders
• For parent folders in Linux mode
–
r
–
x
• For parent folders in ACL mode
–
Traverse / Execute les
–
List folders / Read data
Create les / folders
In addition to the directory check, another check on the
parent folder directly above is required. Users need the
following privileges:
• For parent folders in Linux mode
–
w
• For parent folders in ACL mode
–
Create les / Write data
–
Create folders / Append les
–
Write attributes
–
Write extended attributes
Edit les / folders
In addition to the directory check, another check on the
le or folder itself is required. Users need the following
privileges:
• For parent folders in Linux mode
–
w
• For parent folders in ACL mode
–
Create les / Write data
–
Create folders / Append les
–
Write attributes
–
Write extended attributes
Read les / folders
In addition to the directory check, another check on the
le or folder itself is required. Users need either of the
following privileges:
1. Write privilege
2. Access privileges
• For parent folders in Linux mode
–
r
• For parent folders in ACL mode
–
List folders / Read data
–
Read attributes
–
Read extended attributes
–
Read permissions
Delete les / folders
In addition to the directory check, another check on the
parent folder directly above or the le or folder itself is
required. Users need either of the following privileges:
• For parent folders in Linux mode
–
w
• For parent folders in ACL mode
–
Delete subfolders and les
• For les and folders in ACL mode
–
Delete
Operation
Advanced privilege
disabled
Advanced privilege
enabled
Read (read les
or folders)
Users need to have
at least read-only
privilege to Team
Folder.
Users need to have
at least read-only
privilege for both
ACL and advanced
privileges.
Write (create /
edit / delete les
or folders)
Users need to have
read-write privilege to
Team Folder.
Users need to have
read-write privilege
for both ACL and
advanced privileges.
Table 4
Table 3
Link Sharing Permission
Drive offers two flexible file and folder sharing options, namely,
File Link and Advanced Protection Link, to fulfill the common
corporate needs for exchanging data with internal and external
partners. When files are shared with coworkers within the
company via File Link, a permanent URL is generated for each
file and will not be changed even if the file is renamed or moved
to another folder. Users can share the files and folders that
they have permissions to manage. The customizable sharing
link options allow data to be either shared with specific account
users only, anyone with an account, or anyone with the link.
Abiding by the ACL rules, an entry point is created for a file or
folder to authorize privilege for specific users, internal users, or
public users. The permission setting of a child folder is inherited
from the parent folder. The permission of the child folder can be
changed, but any subsequent changes to the parent folder will
cause the child folder to receive the inherited permissions.
Advanced Protection Link is particularly suitable when sharing
data with partners external to an organization. An URL that
does not abide by the restrictions of ACL rules is created for the
shared files or folders, and this permanent link is examined and
verified each time it is being accessed to ensure data security.
The links can be further protected with passwords and can even
be deleted after the set expiration dates, thereby adding an
extra layer of protection to sensitive and confidential data.

14 Synology White Paper
Syncing, Sharing, and Security
Figure 14: File permissions set with ACL rule
Figure 15: Permission mechanism of Advanced Protection Link
15Synology White Paper
Syncing, Sharing, and Security
Drive ensuresdata security and privacy through enforced
security in data transmission, authentication, and access over
the Internet. For companies frequently engaged in managing
large amounts of file exchange, these features save them the
hassle of additionally encrypting data during each data transfer.
Drive supports the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol during
data transmission to ensure that data are encrypted while
traveling through networks. The support for server certificate
verification allows users to validate the identity of a server
and its administrator before any confidential information is
transferred over the Internet. This verification prevents phishing
site attacks through certificate checks.
In addition to server certificate verification, the Drive client also
tracks the signature of a certificate and issues warnings if the
signature is changed. This mechanism helps the Drive client to
prevent SSL connections from being hijacked (e.g., man-in-the-
middle attack) even if the server is using a self-signed certificate.
As detailed in the Synchronization Mechanism section,
Drive only collects the differences (packed in a patch) between
file versions and transfer file changes by patches, instead of
transferring the entire file upon each update, thereby saving
bandwidth.
Security Mechanism

16 Synology White Paper
Fulfilling Modern Workplace Needs
Fulfilling Modern
Workplace Needs
Designed to fulfill the business needs of today and tomorrow,
Drive comes with full-featured content collaboration tools that
can adapt to workplace scenarios associated with file syncing
and backup, cross-site deployment, hybrid cloud integration,
and more. Its comprehensive integration with other Synology
packages creates a data management ecosystem with multi-
layered security on Synology NAS, unlocking huge value while
overcoming the obstacles to building an on-premise cloud. More
than revolutionizing the concept of data management solution,
Drive also redefines what a NAS can achieve and transforms
Synology NAS into a next-generation file server that can play
a vital role in corporate operations, thereby creating a more
connected, collaborative, and productive workforce.
To experience the powerful tools offered by Drive, please see
this page for the Synology NAS models supporting this package.
Our NAS Selector is designed to he
lp you find the most ideal
NAS product for your corporate environment. Please check out
Compare All NAS Models or contact our sales experts for
more information on the specifications of each NAS model. This
white paper only touches on a portion of the robust features
offered by the multi-functional Synology NAS. To learn more
about Drive and other DSM packages, please try out DSM Live
Demo to experience our technology for free before making the
purchase! Visit our website at www.synology.com or contact
us for product inquiries, technical support, or other assistance.

17Synology White Paper
Fulfilling Modern Workplace Needs
Synology may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Copyright
© 2018 Synology Inc. All rights reserved. ® Synology and other names of Synology Products are proprietary
marks or registered trademarks of Synology Inc. Other products and company names mentioned herein are
trademarks of their respective holders.
synology.com
SYNOLOGY
INC.
9F, No. 1, Yuan Dong Rd.
Banqiao, New Taipei 22063
Taiwan
Tel: +886 2 2955 1814
SYNOLOGY
AMERICA CORP.
3535 Factoria Blvd SE, Suite #200,
Bellevue, WA 98006
USA
Tel: +1 425 818 1587
SYNOLOGY
FRANCE SARL
102 Terrasse Boieldieu (TOUR W)
92800 Puteaux, France
Tel: +33 147 176288
SYNOLOGY
GMBH
Grafenberger Allee 125
40237 Düsseldorf
Deutschland
Tel: +49 211 9666 9666
SYNOLOGY
SHANGHAI
200070, Room 201,
No. 511 Tianmu W. Rd.,
Jingan Dist., Shanghai,
China
SYNOLOGY
UK LTD.
Unit
5 Danbury Court, Linford
Wood, Milton Keynes, MK14 6PL
United Kingdom
Tel.: +44 (0)1908048029
SYNOLOGY
JAPAN CO., LTD.
4F, 3-1-2, Higashikanda, Chiyoda-ku,
Tokyo, 101-0031, Japan
