
© 2019 IJRAR February 2019, Volume 6, Issue 1 www.ijrar.org (E-ISSN 2348-1269, P- ISSN 2349-5138)
IJRAR19VP011
International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR) www.ijrar.org
69
Digitization as a tool for CSR implementation in
Indian Banking Industry: A study on SBI
Ms.Seema Joseph,Assistant Professor,PG Department of Commerce,St.Claret College,Bangalore.
Ms.Rachel Jeslina,Assistant Professor, Bishop Cotton Academy of Professional Management, Bangalore.
Abstract
Digitization, more often, called as Digitalisation is the process of converting data into a digital format
which is more convenient and easy to access and use. Banking industry is universally accepted as the
backbone of any economy, more specifically, a developing economy like India. The health of banking sector
measures the performance of the economy as well. In adhere to the Companies Act provisions on Corporate
Social Responsibility, each bank has their own priority sectors for the CSR spending such as eradication of
poverty, women empowerment, financial inclusion, education, rural development etc. Digitization is not a
new phenomenon, but, its impact on the banking sector is gaining momentum at a faster pace in the world
economy. The definition of banking has witnessed a drastic transformation over the past two decades.
Moreover, the advent of technology has given a new dimension to the corporate social responsibility
activities of the Indian banks. The aim of this paper is to highlight the existing CSR activities undertaken by
the Indian banks. The study also attempts to emphasize on the digitized CSR practices of SBI, the largest
and the oldest public sector bank in the country. The study also shows that majority of the Indian banks are
primarily focussing on the CSR implementation in certain restricted areas and digitisation is totally ignored
in this attempt. Therefore, it is found that there is an increasing need for the banks to take up digital CSR
initiatives to address the sustainability issues in the economy.
Keywords: Corporate Social Responsibility, Digitization, CSR spending, Banking Industry.
Introduction
Digitization is the conversion of data into digital format through the adoption of technology.
Digitization has a major impact on the all aspects of human life and so in the field of business as well. Use of
internet technology has opened the doors to deal with majority of the business activities with ease and
efficiency.Adoption of digitization is very important in the banking industry. Through digitalization, banks
can provide enhanced customer services which is most convenient and time saving. In recent years,
digitization is widely accepted and successfully implemented by the banking industry globally. The key
benefits of digitization are improved business efficiency, huge cost savings, accurate and reliable
performance and faster internal and external processes. In the age of digitization and automation, digitization
of banking is inevitable to catch up the increasing expectations of the society in which it exist. Globally,
enterprises are going digital at a faster pace to stay ahead of the competition. All the service sector
enterprises like insurance, healthcare, hospitality, retail and their global congloromates are all on the march
to quirkily adopt digitization across branches. Banking is one of those service sector industries which has
undergone a massive digital shift in all its functions.
Social responsibility refers to the responsibility of business towards the society in which it exist. The word
responsibility implies that the business has moral obligation towards the society over and above the statutory
requirements which benefits the society and in turn the business. The term corporate social Responsibility is more
commonly called as corporate conscience, corporate citizenship, corporate sustainability etc. The world
business council for sustainable development defines CSR as “the continuing commitment by business to
behave ethically and contribute to economic development while improving the quality of life of the
workforce and their families as well as of the local community and society at large.” Corporate Social
Responsibility is basically a form of corporate self-regulation integrated into a business model.
Now internet has made a way to economically promote it and gain space in the positive side of mind
set of people. CSR has taken a paradigm shift with the advent of technology and digitization and the
stakeholders are greatly benefited by the improved CSR activities of the banks. Today Banking Sector
© 2019 IJRAR February 2019, Volume 6, Issue 1 www.ijrar.org (E-ISSN 2348-1269, P- ISSN 2349-5138)
IJRAR19VP011
International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR) www.ijrar.org
70
growing larger and powerful than before. CSR defined as “the economic, legal, ethical, and philanthropic
expectations placed on organizations by society at a given point in time.” (Carrol and Buchholtz, 2000:35).
Exactly what responsibility companies have towards society has been discussed for some decades now.
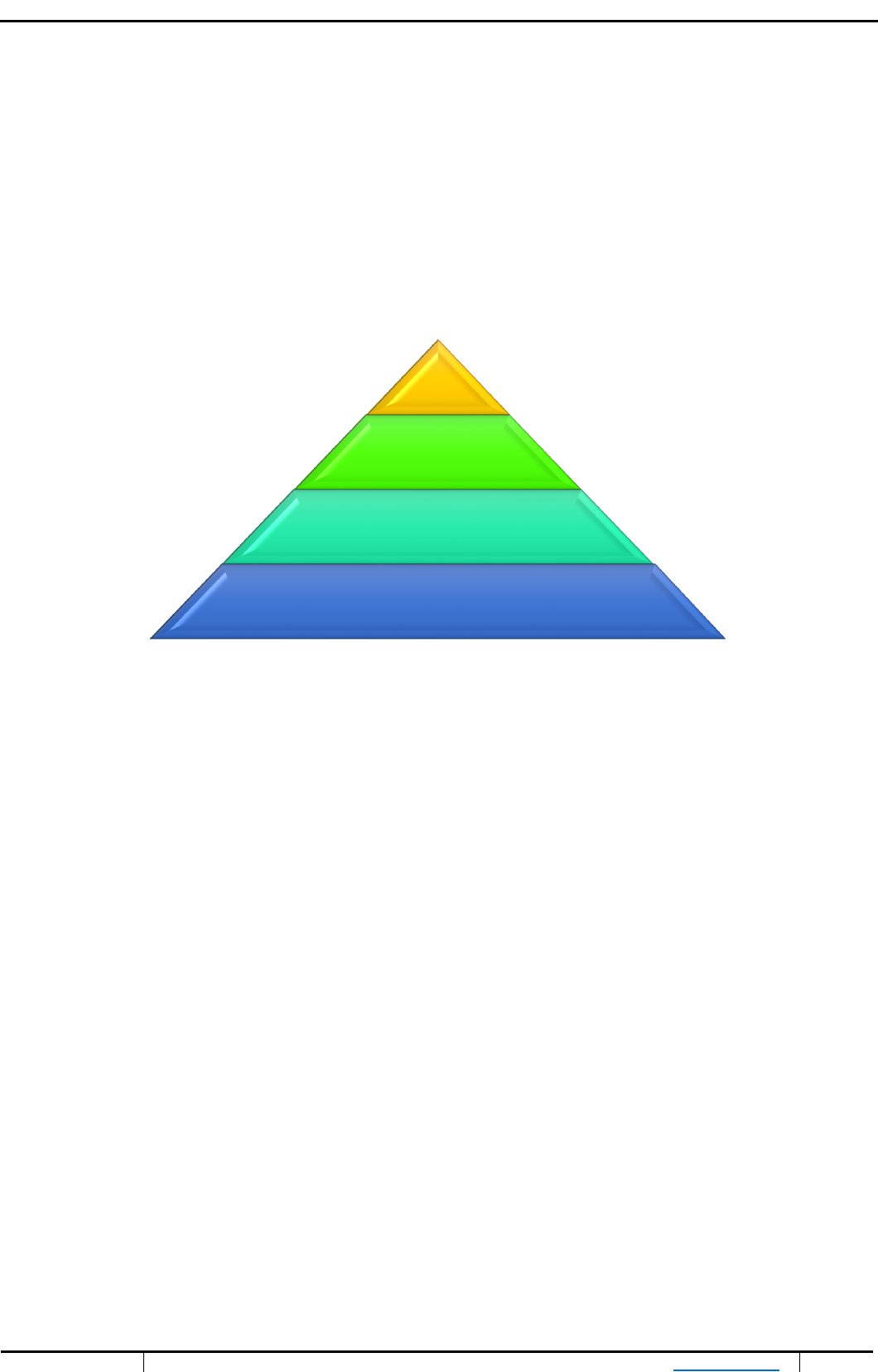
Economic responsibilities: The first responsibility of the company towards society refers to running the
business as an economically healthy unit. It includes aspects such as return on investment for shareholders,
fair employee salaries, and quality products supplied to customers at fair prices; all required by the society.
(Crane & Matten, 2004)
Ethical responsibilities: It refers to corporation’s responsibilities which are not covered by legal or
economical requirements, but instead by what could be considered as fair in the eyes of society. Society
therefore expects corporations to act ethically towards their stakeholders. (Crane & Matten, 2004)
Chart 1. Carroll’s four-part model of corporate social responsibility (Carroll, 1991)
Legal responsibilities: Demands that companies act in accordance with existing legislation and regulatory
requirements. The legal framework consequentially fosters society’s ethical view and all companies
attempting to be socially responsible are therefore required by society to follow the law. (Crane &Matten,
2004)
Philanthropic responsibilities: This involves corporation’s willingness to enhance the quality of living for
their stakeholders (i.e. employees, local community, and society at large) through charitable donations and
organizational support. These corporate decisions are entirely voluntary, of less importance than the former
three, and (with regards to social responsibility) only seen as desired by society. (Crane & Matten, 2004).
Literature Review
As per the RBI norms, it is the ethical responsibility of the banks to pay special attention towards
integration of social and environmental concerns in their business operations. Stressing the need for
Corporate Social Responsibility, RBI pointed out that these initiatives by the banks are vital for sustainable
development. On the basis of the review of literature, it is very important to note that the banks are required
to take conscious efforts to indulge in the CSR activities at a faster pace than earlier.
Saxena (2016) in his study on the selected public and private sector banks analyses that though the Indian
banks are making efforts in CSR initiatives , they still need to take more conscious efforts on CSR. It was
also found that some of the banks do not adhere to the regulatory directions of RBI in this regard.
Sharma and Agarwal (2016) in their study based on secondary data on 12 public sector banks & 7 private
sector banks revealed that the CSR expenditure as a percentage of PAT of the Indian companies is much
below the statutory requirement of 2% . It is also found that there is no significant difference between the
trend of CSR spending of Public sector companies & Private sector companies in India.
Juman and Christopher (2016) in their study on Indian banks analyses that banks are more responsible
for addressing the social issues concerning the local community and financial inclusion is the focal point of
Philanthropic
responsibilities
Ethical responsibilities
Legal Responsibilities
Economic Responsibilties

© 2019 IJRAR February 2019, Volume 6, Issue 1 www.ijrar.org (E-ISSN 2348-1269, P- ISSN 2349-5138)
IJRAR19VP011
International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR) www.ijrar.org
71
their social responsibility activities. On the contrary, it is also found that environmental issues remain
ignored by many of the banks. Further, the total income and size of banks play a very significant role in
CSR contribution where, banks with higher income contributes better towards their CSR initiatives.
Hossain and Khan (2016) in their research paper entitled “Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in
Banking Sector: An Empirical Study on the Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC)
Limited” they inspected the people expectation and the response of the Bank and they viewed that the sum
contributed by HSBC for CSR activities is expanding but the growth rate is slow.
Csaba Lentner, Krisztina Szegedi, Tibor Tatay (2015) in their study on “Corporate Social responsibility
in the Banking Sector” , made a conceptual study on the CSR strategies of banks. This paper discussed
corporate social responsibility (CSR), as an attitude putting ethical norms as the focal point. The paper also
points out that ethical responsibility is the obligation to conduct in a fair way and to do the right thing.
Singh Namrata (2015) in her paper tries to focus on the new concept of Corporate Social Responsibility and
how banks are adopting this practice in their working. In the recent time banking sector is one of the
emerging sector which contributes a lot in the development of the nation by providing their support towards
the education. Banks are expending every year some amount for educating the people, stressing on the basic
logic, if the people are educated then the nation will be developed.
Sapna Katara, Dr. Lokesh Arora (2014) in their study entitled “ Emerging trends in CSR in Indian banks”
analyses that the banks are making conscious efforts for the implementation of CSR as a business model .But inspite
of their efforts to follow the changing trends in CSR, they are restricted with certain limitations. The authors in their
study opines that there is a need to better CSR activities by the banks, which is possible by making it more
systematized and integrated with the changing global perspective and social scenario.
Rajput, Kaura and Khanna (2013) in their study entitled “Indian banking sector towards a sustainable
growth: a paradigm shift” have made an attempt to analyze the response of the Indian banks towards the
social issues concerning the stakeholders at large. And it was found that Indian banks have been rather slow
in responding to the sustainability concerns and issues, amidst the associated risks and the challenges to
create new business avenues.
Research Objectives
The major objectives of this paper are:
1. To examine the major areas focussed by the Indian banks for CSR implementation.
2. To analyse the digitized CSR practices of the leading public sector bank, ie., State Bank of India.
Methodology
The study is based on the secondary data collected from the disclosed annual reports, corporate
sustainability reports, journals, magazines, websites etc. Standard books and articles were also referred to
collect valuable information about the CSR practices of Indian banks. The CSR practices of five commercial
banks randomly picked from the public and private sector were also analysed for the purpose of the study.
The present study primarily covers the largest public sector bank, ie, State Bank of India. The State bank was
chosen for the study based on profitability, deposits, net worth, number of account holders and the digital
CSR practices.
Data Analysis
Regulatory Framework of CSR In India
In India, Companies Act, 2013 has introduced the idea of CSR to the forefront and the Act provides
greater transparency and disclosure through its mandate. Schedule VII of the Companies Act lists out the
CSR activities and suggests the communities to be the focal point. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs as
notified in Sec 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 as well as the provisions of the Companies (CSR Policy)
Rules, 2014, every company, private limited or public limited, which either has a net worth of Rs. 500 crore
or a turnover of Rs 1,000 crore or net profit of Rs.5 crore, needs to spend at least 2% of its average net profit
for the immediately preceding three financial years on corporate social responsibility activities. During the
financial year such a company shall constitute a CSR committee of the Board consisting of three or more

© 2019 IJRAR February 2019, Volume 6, Issue 1 www.ijrar.org (E-ISSN 2348-1269, P- ISSN 2349-5138)
IJRAR19VP011
International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR) www.ijrar.org
72
directors, out of which at least one director shall be an independent director. The CSR committee shall
formulate and recommends to the Board, a CSR Policy which shall include the activities to be undertaken by
the company as specified in the schedule VII, recommend the amount of expenditure to be incurred in those
activities, as well as monitor the CSR Policy of the company from time to time. The major thrust areas of
CSR activities as per Schedule VII of Companies Act, 2013 are eradicating hunger, poverty and
malnutrition, promoting preventive healthcare, promoting education and promoting gender equality,
setting up homes for women, orphans and the senior citizens, measures for reducing inequalities faced by
socially and economically backward groups, ensuring environmental sustainability and ecological
balance, animal welfare, protection of national heritage and art and culture and a lot more. However, in
determining CSR activities to be undertaken, preference should be given to local areas and the areas around
where the company operates.
KEY AREAS FOR CSR ACTIVITIES IN INDIAN COMMERCIAL BANKS
Schedule VII of Sec. 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 points out the activities which may be included
in CSR and the banks are in their attempts to strictly adhere to this. It is found that both the public and
private sector banks have given utmost importance to the priority sector lending, apart from meeting
demands of the industry.
Priority sector lending include; agriculture, rural development, education loan, housing loans, health
care, community welfare and finance to weaker sections of the society. The CSR activities primarily
comprise the following:
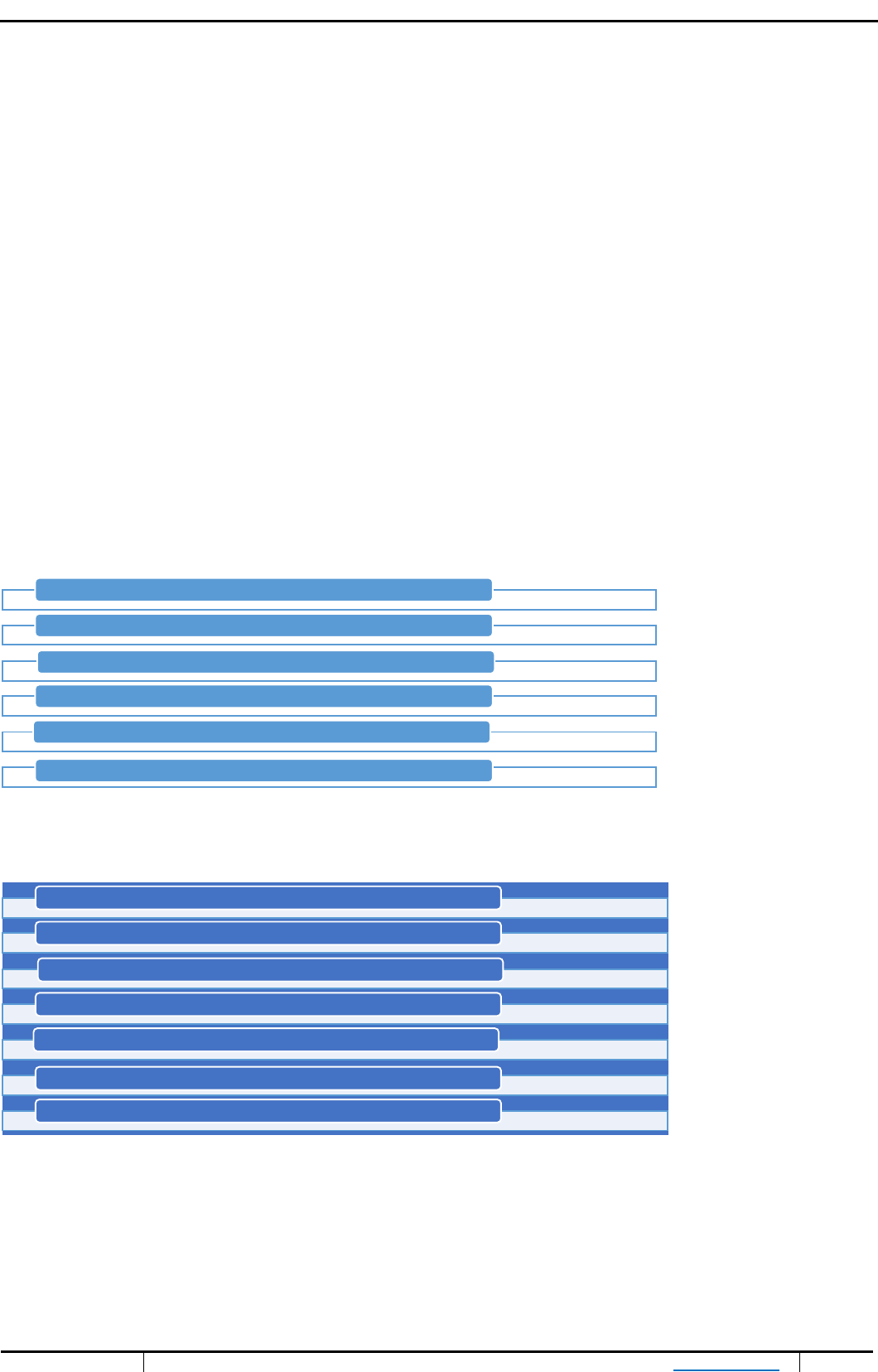
Chart 2. Core areas of CSR in Public Sector Banks
Source: Compiled by the author based on secondary data
Chart 3. Chart 3. Core areas of CSR in Private Sector Banks
Source: Compiled by the author based on secondary data
Digital CSR Initiatives of State Bank of India
The State Bank of India, popularly known as SBI, is India’s largest commercial bank with a strong
legacy of over 200 years. It is the oldest commercial bank in the Indian sub-continent, strengthening the
trillion-dollar economy of the nation. SBI is the largest bank in terms of assets, deposits, profits, branches,
number of customers and employees, enjoying the continuing faith of millions of customers across the country.
The concept of CSR was introduced in the State Bank of India in the early 1970’s. And the bank was
Education
Community Welfare
Poverty Eradication
Women Empowerment
Rural Development
Vocational Training
Health care
Rural development
Community Welfare
Child Welfare
Education and employment
Environment Protection
Responsible Banking

© 2019 IJRAR February 2019, Volume 6, Issue 1 www.ijrar.org (E-ISSN 2348-1269, P- ISSN 2349-5138)
IJRAR19VP011
International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR) www.ijrar.org
73
involved in activities which contributed to the common good of th society such as blood donation camps,
health camps, participation in local festivals, adult literacy, tree planting etc.
SBI is the first bank to begin with the CSR activities much before the statutory guidelines of RBI and
the government. They had the practice of using some part of their profit to the noble cause of development,
advancement of society, employment generation etc. The CSR philosophy of SBI stems from the belief that
bank is a corporate citizen which derives resources and benefits from the society. Therefore, it is the moral
responsibility of the bank to serve the under-privileged and less –fortunate of the same society. The bank
also encourages the staff members to make their contribution towards this noble cause will lead to their self-
development and improvement of the Bank’s image besides development of the Community.
The Sustainability Development journey of SBI is built upon the three key pillars of Social Responsibility,
Environmental Responsibility and Economic Responsibility. The CSR policy of State Bank of India is committed
to:
Enhancing stakeholder’s value though value-driven engagement.
Economic and social well-being of the society, particularly the less fortunate and under-privileged
members of the society.
Minimize the direct and indirect impact of its operations on the environment.
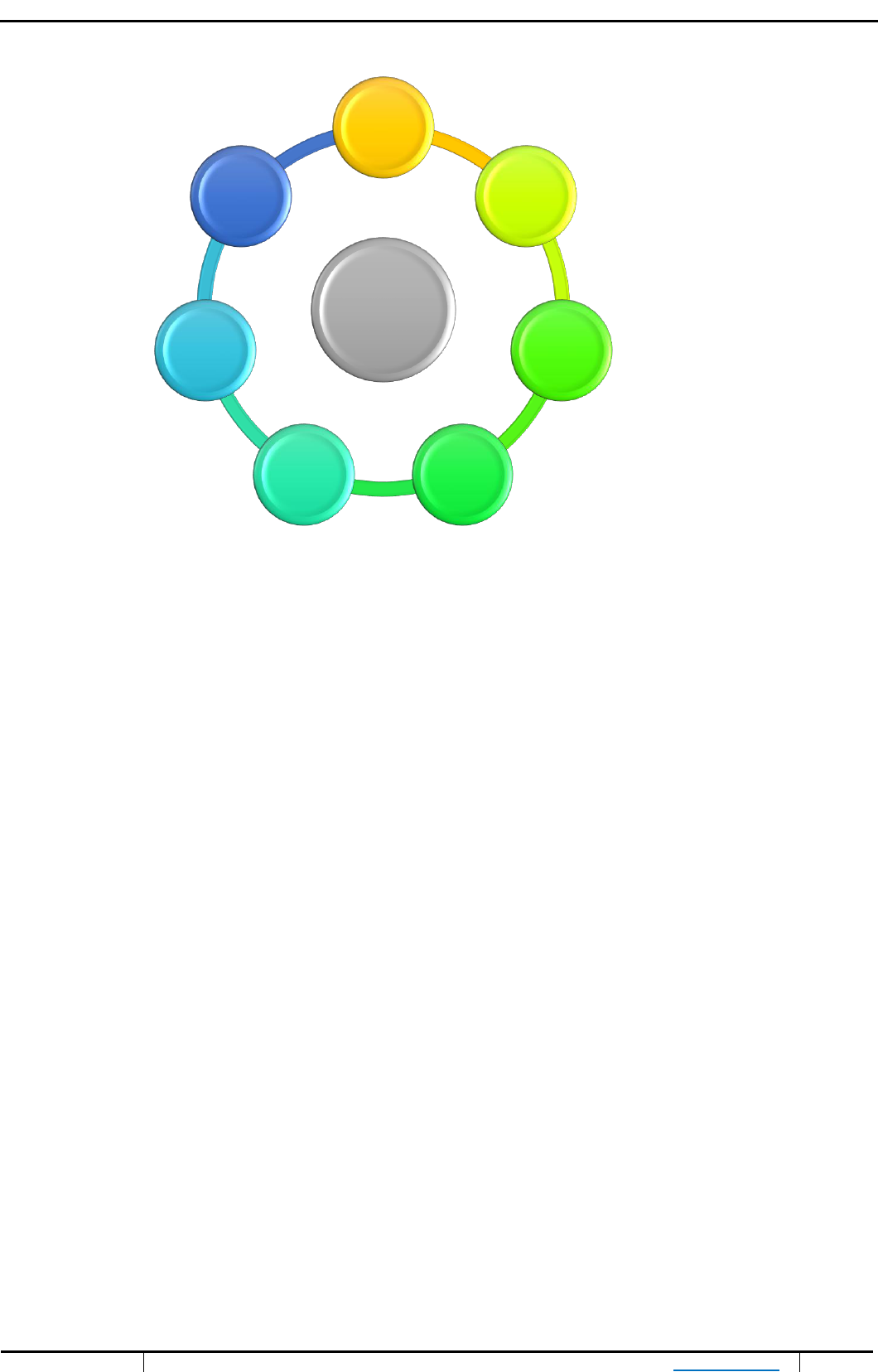
Over the past few years, SBI has been focussing on certain CSR implementation areas which can be
broadly classified into five categories namely, Supporting healthcare, Supporting education, Livelihood
creation, Support during Natural calamities and Financial Inclusion.
Chart 4. Core areas of CSR implementation of SBI
Source: Compiled by author on the basis of secondary data
Digital CSR Products of SBI
SBI has introduced the Digital CSR products to enhance customer experience as a step forward towards it CSR
implementation strategies. The primary goal of SBI CSR digital products is to provide simpler, faster & easier
access to all the products & services offered by the banks.
As part of Modernisation and technological innovation, SBI has added seven digital products , adding a new
segment to its CSR implementation. Some of the most prominent digital CSR services of SBI are as follows:
CSR
Health
Care
Financial
Inclusion
EducationLivelihood
Natural
Calamities
© 2019 IJRAR February 2019, Volume 6, Issue 1 www.ijrar.org (E-ISSN 2348-1269, P- ISSN 2349-5138)
IJRAR19VP011
International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR) www.ijrar.org
74
Chart 5. Digital CSR initiatives of SBI
Source: Compiled by the author based on Sustainability Report of SBI (2016-17)
SBI digital village
State Bank of India has introduced its integrated CSR initiative SBI DIGITAL VILLAGE under the SBI
Foundation in 2017.SBI Digital Village is a comprehensive initiative to create a cashless ecosystem in every
village. It also provides an approach to Government supported digital initiatives in health, agri-schemes & social
security, educations, subsidies, and benefits. Initially, this facility is being implemented in the selected 21 villages
across the nation. Through Digital Village, the bank can connect people by providing Net banking, ATM cards,
Green channel banking, Mobile banking, Self-service passbook printing machines, Wallet banking, POS, Cash
Deposit Machines and Micro ATM at the village locations. Digital Village aims to improve the standard of
people especially in villages and is considered as a part of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR).
SBI BUDDY
State bank buddy is a mobile wallet app that allows the users to send or ask for money from any of the
contacts even if they do not have an account with SBI. It is a unique blend of payment and banking service. SBI
Buddy is the best in market-wallet and has radical collaborations with merchant partners for exceptional shopping
and payment experience. With the help of State Bank Buddy, the users have the freedom to recharge
mobile/DTH, pay bills, book bus/flight/movie tickets, and send money to anyone 24×7 on the move.
SBI Digi voucher
SBI Digi voucher is a green initiative of SBI that allows the customers to access online to various forms,
transaction slips and /challans through an APP. It also saves your valuable time to get direct access to the teller
counter by allowing them to pre-complete transactions online.
SBI mingle
SBI Mingle is the social banking app which permits the users to perform the basic banking activities via
SBI official page. It provides the convenience of banking on Twitter and Facebook through an App-based
interface. Customers can perform all transactions anytime and anywhere just by logging in to their social media
account.
SBI
Digital
CSR
Initiatives
SBI
Digital
village
State
Bank
Buddy
State
Bank
Scribe
SBI Digi
voucher
SBI
video
Statemen
t
SBI
smart
Watch
SBI
Mingle

© 2019 IJRAR February 2019, Volume 6, Issue 1 www.ijrar.org (E-ISSN 2348-1269, P- ISSN 2349-5138)
IJRAR19VP011
International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR) www.ijrar.org
75
SBI scribe
State Bank Scribe is a unique, first of its kind service offered by SBI. SBI Scribe is an innovative real
time digitization platform that captures all the customer information in one go. It is handwritten and enables
immediate account activation. On July 1, 2016, the 61st SBI Bank day, SBI introduced SBI Scribe to provide
every customer a digital and easy banking experience. SBI is now able to open user account by capturing the data
digitally and verifying the data entered in real time thereby improving overall banking experience with SBI. SBI
values customer time and user experience. Customers can use the same pen and paper that they are comfortable
with to fill the application form. SBI has built in technical smarts (intuitive user interface) to take care of the
rest.SBI Scribe is a convenient and user friendly account opening process that enables immediate account
activation. SBI Scribe is simpler, faster and easier. The traditional wait for account opening is now history.
There is no more delayed account opening process and no more long queues. Customers can now visit the
nearest SBI branch and open an account in a jiffy. SBI Scribe is a step closer to being The “ Banker to
Digital India”.
SBI smart watch
SBI Smart Watch allows banking through the state bank smart watch which offers a unique banking
experience in tune with the technology of the future. SBI Smart Watch App is a unique digital App which
will help the customers to check their account statements, last transaction etc. anywhere across the world.
SBI Video statement
It is an innovative digital CSR plan of the bank to allow the visually challenged customers to view
their account statement. The account statement is available wit dashboards and spend analysis with a
friendly audio narration.
SBI Yono
SBI YONO app is an integrated digital banking platform that enables the users to access a variety of
financial services and other services such as online shopping, taxi bookings, travel planning, offline retail,
online education, or medical bill payments. With YONO, customers only need one application for all the
mobile banking services such as cashless bill payments, loans, fund transactions, & bank account opening,
investments, insurance and daily shopping needs
Conclusion
The study shows that Social Responsibility is one of the primary focus areas for all the commercial
banks in recent years. Majority of the banks are concentrating on the thrust areas of social responsibility as
prescribed by the companies Act, 2013.But the study reveals that that very few banks have tried to adopt
digitization into their responsibility practices. Since digitization is very important in the banking sector akin
to any other sectors of the economy, it is inevitable for the banks to integrate technology into their CSR
practices. In the age of digitization and automation, digitization of banking is inevitable to catch up the
increasing expectations of the society in which it exist. Globally, enterprises are going digital at a faster pace
to stay ahead of the competition. All the service sector enterprises like insurance, healthcare, hospitality,
retail and their global congloromates are all on the march to quirkily adopt digitization across branches. The
digital CSR practices of SBI is worth appreciable in this regard. As the largest bank in the Indian sub-
continent, SBI has actually set the standard for all the other conglomerates to follow.
The advent of technology demands more innovative and digitized CSR initiatives from the commercial
banks. The banking system have already taken the toll the is now focussed on digitization of their services and
also attempt to reach the banking services even to the remote villages of the country. Now the main challenge to
be faced by the banks is to link the technology to the CSR practices to create a better experience for the
community.
With a concentrated approach, it is possible to channelize the CSR strategies of the commercial banks towards an
inclusive growth by the collaborative use of digital technology.Therefore, it is advisable for the commercial
banks to take greater efforts to enhance and accelerate the digital CSR initiatives of commercial banks to ge a
competitive edge in terms of sustainability and development of the industry and community at large.

© 2019 IJRAR February 2019, Volume 6, Issue 1 www.ijrar.org (E-ISSN 2348-1269, P- ISSN 2349-5138)
IJRAR19VP011
International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews (IJRAR) www.ijrar.org
76
References
1. Saxena, S. (2016). A Comparative study of corporate social responsibility (CSR) of private and
public sector banks. World Wide Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Development 2(1) , 21-
23.
2. Sharma, S. K., & Agarwal, A. (2016). Comparative study of Corporate Social Responsibility in
Selected Public and Private Sector Banks. BRDU international journal of multidiscplinary research
1(3) , 10-17.
3. S. Hossain, & R. Khan (2016) Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in Banking Sector: An
Empirical Study on the Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC) Limited, IOSR
Journal of Business and Management,18(4), , 53-61.
4. K, M. J., & Christopher, D. J. (2016). Corporate social responsibility: an analysis of indian banks.
International Conference on "Research avenues in Social Scienceǁ Organize by SNGC,
Coimbatore1(3) , 129-135.
5. Nidhi, (2016): “Corporate social responsibility in indian banking industry: study on attempts of HDFC bank”
International Journal of Research – Granthaalayah, Vol. 4, No. 8 62-74.
6. Dastidar Sumee (2016). Essence of corporate social responsibility in select Indian commercial banks.
International Journal of Applied Research 2016; 2(1): 164-169.
7. Namrata Singh, Dr.Rajlaxmi Srivastava and Dr. Rajni Rastogi,(2015) Lighting the Lamp of Education: Role
of Indian Banking Sector towards the Corporate Social Responsibility in achieving Development Goals
(International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Research ISSN: 2321-3124)
8. Csaba Lentner, Krisztina Szegedi,Tibor Tatay (2015) , Public Finance Quarterly, 2015, vol. 60, issue 1, 95-
103.
9. Sapna Katara, Dr. Lokesh Arora(2014),” Emerging trends in CSR in Indian banks” International
Journal of Multidisciplinary Consortium Volume – 1,Issue – 3,December 2014
ijmc.editor@rtmonline.in| http://ijmc.rtmonline.in | ISSN 2349-073X.
10. D. Dhingra, & R. Mittal(2014) CSR Practices in Indian Banking Sector, Global Journal of Finance
and Management, 6(9),853-862.
11. Rajput, D. N., Kaura, M. R., & Khanna, M. A. (2013). Indian banking sector towards a sustainable
growth: a paradigm shift. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social
Sciences 3(1).
12. Sarita Moharana,(2013) Corporate Social Responsibility: A Study of Selected Public Sector Banks in India
13. Das, B. K., & Halder, P. K. (2011). Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives of Oils PSUs in Assam: A Case
study of ONGC. Management Convergence , 2 (2), 75-85. 16.
14. Carroll, A. B. (2008). A History of Corporate Social Responsibility: Concept and Practices.
15. Agrawal, Sanjaoy K,” Corporate Social Responsibility in India “(2008) Response Business Book from Sage,
Sage Publications, New Delhi.
16. Crane, A. Mc Williams, D. Matten, J. Moon, & D. Siegel, The Oxford Handbook of Corporate Social
Responsibility (pp. 19-46). New York: Oxford University Press.
17. Carroll, A. B. (1999). Corporate Social Responsibility Evolution of a Definitional Construct. Business &
Society , 38 (3), 268-295.
18. International Journal of Applied Research 2016; 2(1): 164-169
19. Sustainability Reports 2016-17 of SBI and ICICI
20. Websites of different banks
21. Baxi, C V & Prasad Ajit (Ed) (2005), Corporate Social Responsibility-Concept and Cases, New Delhi, Excel
Books.
